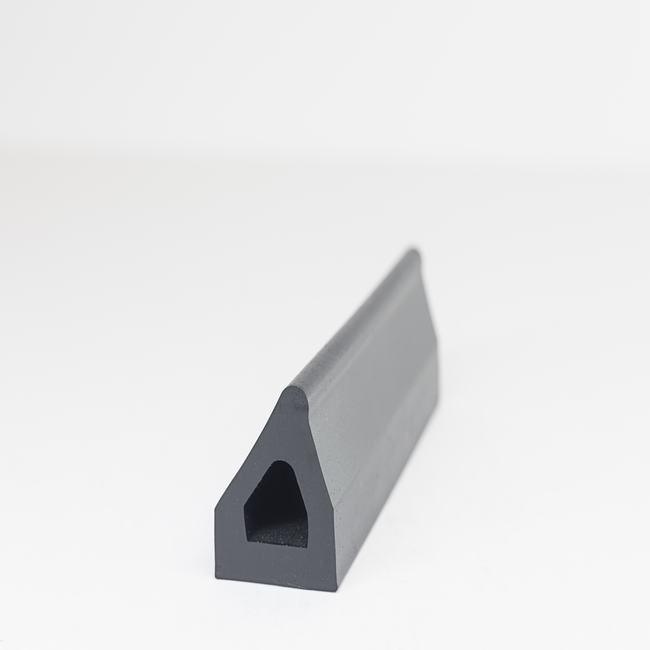
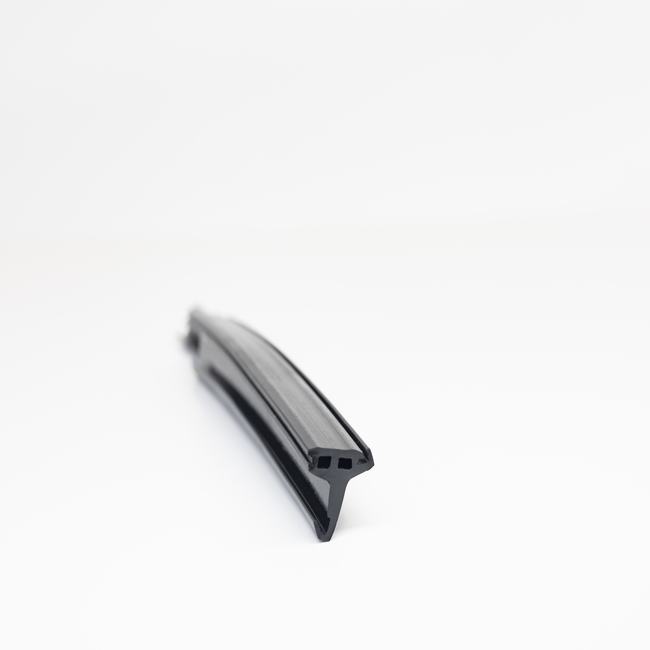
EPDM (Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer) rubber gaskets are widely used sealing components in various industries and applications. EPDM is a synthetic rubber known for its excellent resistance to weathering, UV radiation, ozone, and a wide range of chemicals. EPDM rubber gaskets are designed to provide effective sealing, insulation, and protection against environmental factors. Let’s delve into a detailed description of EPDM rubber gaskets, covering their construction, properties, applications, and benefits.
Construction and Materials:
EPDM rubber gaskets are typically manufactured using a vulcanization process, which involves cross-linking the EPDM polymer chains with sulfur or other cross-linking agents. This process enhances the rubber’s resilience, flexibility, and resistance to environmental factors. EPDM gaskets may also include reinforcing elements, such as fabric or metal inserts, to improve their strength and stability.
Properties and Characteristics:
EPDM rubber gaskets possess a range of valuable properties:
- Weather Resistance: EPDM gaskets excel in outdoor applications due to their outstanding resistance to weathering, UV radiation, and ozone exposure. They maintain their integrity and sealing capabilities in harsh environmental conditions.
- Chemical Resistance: EPDM is known for its resistance to a wide range of chemicals, acids, bases, and polar solvents. This property makes EPDM gaskets suitable for use in various industrial settings.
- Temperature Tolerance: EPDM rubber remains flexible and functional across a broad temperature range, from -40°C (-40°F) to 150°C (302°F). This versatility allows for both low-temperature sealing and high-temperature insulation.
- Resilience and Compression Set Resistance: EPDM gaskets maintain their shape and sealing properties even after compression and release, preventing permanent deformation known as “compression set.”
- Electrical Insulation: EPDM rubber has excellent electrical insulating properties, making it suitable for use in electrical enclosures and gaskets.
- Low Gas Permeability: EPDM exhibits low gas permeability, which is beneficial for sealing applications, preventing the escape of gases or the intrusion of contaminants.
- Tensile Strength: EPDM rubber possesses good tensile strength, which contributes to its durability and resistance to tearing or ripping.
Applications:
EPDM rubber gaskets are employed in a wide range of industries and applications, including:
- Automotive: EPDM gaskets are used in automotive applications, such as door seals, window seals, and under-the-hood gaskets, for their weather resistance and durability.
- Construction: In the construction industry, EPDM gaskets serve as weatherstripping, expansion joint seals, and roofing seals to prevent water infiltration and maintain energy efficiency.
- HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning): EPDM gaskets are utilized in HVAC systems for duct sealing, vibration damping, and insulation.
- Electrical Enclosures: EPDM gaskets provide electrical insulation and environmental protection in electrical enclosures, control panels, and junction boxes.
- Aerospace: In the aerospace sector, EPDM gaskets are used in aircraft windows and seals due to their resistance to extreme temperatures and UV radiation.
- Marine: EPDM gaskets are used in marine applications, including boat hatches, portholes, and seals, where they must withstand exposure to saltwater and sunlight.
- Industrial Manufacturing: Various industrial equipment and machinery incorporate EPDM gaskets for sealing, insulation, and chemical resistance.
- Food and Beverage: EPDM rubber gaskets are used in food and beverage processing equipment because of their compatibility with food-grade applications and sanitation requirements.
In conclusion, EPDM rubber gaskets are versatile sealing components with a wide range of applications across industries. Their exceptional weather resistance, chemical resistance, temperature tolerance, and electrical insulation properties make them valuable for sealing, insulation, and protection in diverse settings, contributing to improved product performance and longevity.