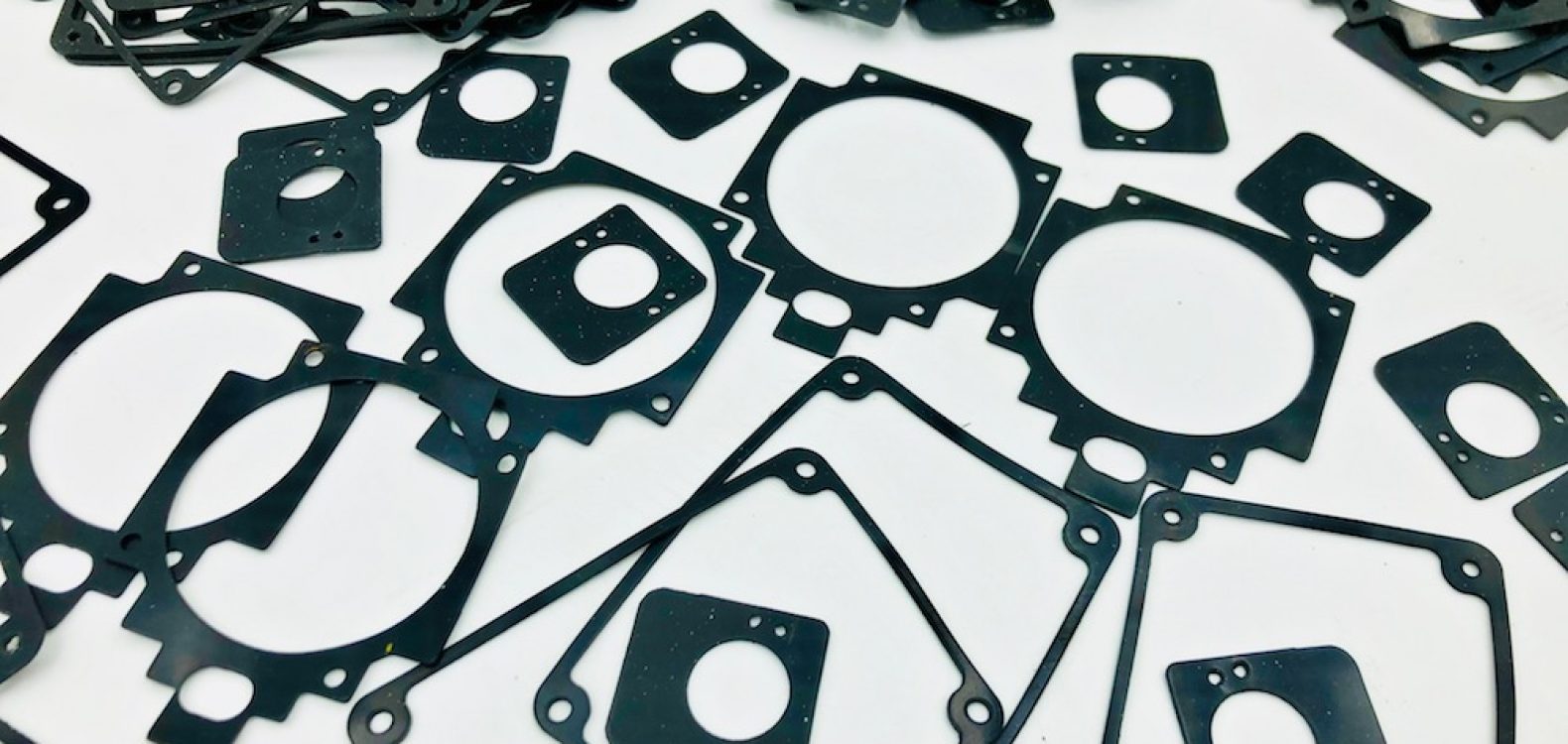
Industrial seals are critical components in a wide range of industrial applications, serving the essential function of preventing leaks, protecting machinery, containing fluids, and maintaining the integrity of various systems. These seals are designed to withstand harsh operating conditions, extreme temperatures, high pressures, and aggressive chemicals. In this comprehensive description, we will explore the various aspects of industrial seals, including their functions, types, materials, applications, and the industries where they are commonly used.
Functions of Industrial Seals:
- Leak Prevention: One of the primary functions of industrial seals is to prevent leaks of fluids or gases. Whether in hydraulic systems, pipelines, or process equipment, seals ensure that materials stay contained and do not escape, which is crucial for safety, environmental compliance, and operational efficiency.
- Environmental Protection: Industrial seals protect the surrounding environment from the substances within industrial equipment. This is vital to prevent contamination, pollution, and the release of hazardous materials.
- Component Protection: Seals help safeguard critical components, such as bearings, gears, and shafts, from exposure to dust, debris, and harsh conditions. This extends the lifespan of machinery and reduces maintenance requirements.
- Friction Reduction: Seals reduce friction between moving parts, which can enhance the efficiency and performance of industrial equipment, as well as reduce energy consumption.
- Shock and Vibration Dampening: In some applications, seals are used to absorb shock and vibration, preventing damage to equipment and ensuring smooth operation.
- Heat and Temperature Resistance: Industrial seals are designed to withstand extreme temperatures, whether in high-temperature industrial processes or cryogenic applications.
Types of Industrial Seals:
- O-Rings: O-rings are circular seals that are commonly used in dynamic and static applications. They are versatile and available in various materials, making them suitable for a wide range of industries.
- Gaskets: Gaskets are flat seals used to create a seal between two flat surfaces. They are often made from materials like rubber, paper, metal, or composite materials.
- Mechanical Seals: Mechanical seals are used in rotating equipment, such as pumps and mixers, to prevent leakage. They consist of two primary components, a stationary and a rotating part, that are pressed together to create a seal.
- Lip Seals: Lip seals, often used in rotary shafts, have a flexible lip that contacts the surface of the rotating shaft, preventing leaks and contaminants from entering the housing.
- Diaphragm Seals: Diaphragm seals are used in pressure measurement instruments and isolate the process fluid from the sensor, protecting the sensor from harsh or corrosive materials.
- Hydraulic Seals: Hydraulic seals are designed for use in hydraulic systems to prevent fluid leakage and maintain the pressure required for hydraulic machinery to function effectively.
Materials Used:
Industrial seals can be manufactured from a wide range of materials, each chosen for its specific properties and the demands of the application. Common materials include:
- Rubber: Nitrile, silicone, EPDM, and fluorocarbon rubber are frequently used for their flexibility and resistance to various chemicals and temperatures.
- Metal: Stainless steel, aluminum, and other alloys are used for gaskets and high-temperature, high-pressure applications.
- Plastics: PTFE (Teflon), polyurethane, and other plastics are utilized for their chemical resistance and low-friction properties.
- Composites: Some seals are made from composite materials that offer a combination of properties, such as resistance to heat and chemicals.
Applications:
Industrial seals are integral to a wide range of industries and applications, including:
- Oil and Gas: Seals are used in drilling equipment, pipelines, and refineries to prevent leaks and protect against harsh environmental conditions.
- Aerospace: In aircraft and spacecraft to maintain cabin pressure, protect sensitive components, and ensure safety during extreme conditions.
- Automotive: Seals are found in engines, transmissions, and other critical automotive components to prevent leaks and ensure optimal performance.
- Manufacturing and Processing: Used in a variety of manufacturing equipment, such as pumps, mixers, and hydraulic systems, to prevent fluid leakage and maintain efficiency.
- Pharmaceuticals and Food Processing: In machinery used for the production and packaging of pharmaceuticals and food products, where hygiene and containment are critical.
- Chemical and Petrochemical: In pumps, valves, and vessels to prevent leaks and ensure the safe handling of corrosive and hazardous chemicals.
- Power Generation: In power plants, including nuclear, coal, and natural gas facilities, to maintain the integrity of various systems under extreme conditions.
- Construction and Infrastructure: Used in infrastructure components like bridges, dams, and tunnels to maintain structural integrity and prevent water ingress.
- Marine and Offshore: In maritime equipment, such as ships and offshore platforms, to withstand saltwater, extreme pressures, and harsh environmental conditions.
In summary, industrial seals are indispensable components in various industries, providing essential functions like leak prevention, environmental protection, and component safeguarding. They come in various types and materials to meet the specific demands of different applications, ensuring safety, efficiency, and reliability across a wide range of industrial processes and equipment.